The role of the administrator in HRM¶
Technical features¶
HRM consists of two main components: a web based interface and a queue manager.
The web interface allows:
- the management of users by the system administrator;
- the management of parameter sets (templates) that all users can copy or use directly;
- the creation of deconvolution jobs, including image selection, setting microscopic, restoration and analysis parameters;
- inspecting the job queue status, and allowing the users to delete their own jobs from it;
- previewing and analyzing deconvolved images, including a slicer, MIP and SFP renderers, movies and colocalization results;
- sharing templates among users;
- visualizing user and jobs statistics.
HRM is equipped with a simple http file uploader/downloader to send raw images from the user’s local machine to the HRM server, as well as to retrieve the deconvolution results from the server. The server administrator can set up a limit for these transactions.
The queue manager, running the background, dispatches:
- the jobs created via the web interface to any of the dedicated servers running Huygens Core.
- the emails to inform the users that the job is finished and that the restored datasets are available.
Installation and requirements¶
To install HRM the following pre-requisites (at least) must be fulfilled:
- Operating system: Any recent Linux distribution. Based on Debian or RHEL.
- Huygens Core: HRM is just an interface and needs Huygens Core to perform deconvolution on the raw images. Note that Huygens Core needs a license.
- Apache2 web server.
- PHP version ≥ 5.6: Both the HRM queue manager and the web interface are written in PHP and need PHP to operate.
- MySQL or PostgreSQL: A relational database management system is required to store deconvolution parameters, job descriptions and, optionally, user accounts.
- A file server: To temporarily store input and restored datasets.
The setup is highly configurable, since the file server, the processing servers and the queue manager can either be all hosted by the same machine or be distributed across two, three or more computers.
To follow the steps for a guided installation please see the installation page at the HRM project’s site.
Administrator’s options¶
Log in to HRM with the credentials of the administrator. Instead of the regular user home panel HRM will display the administrator home panel, like this:
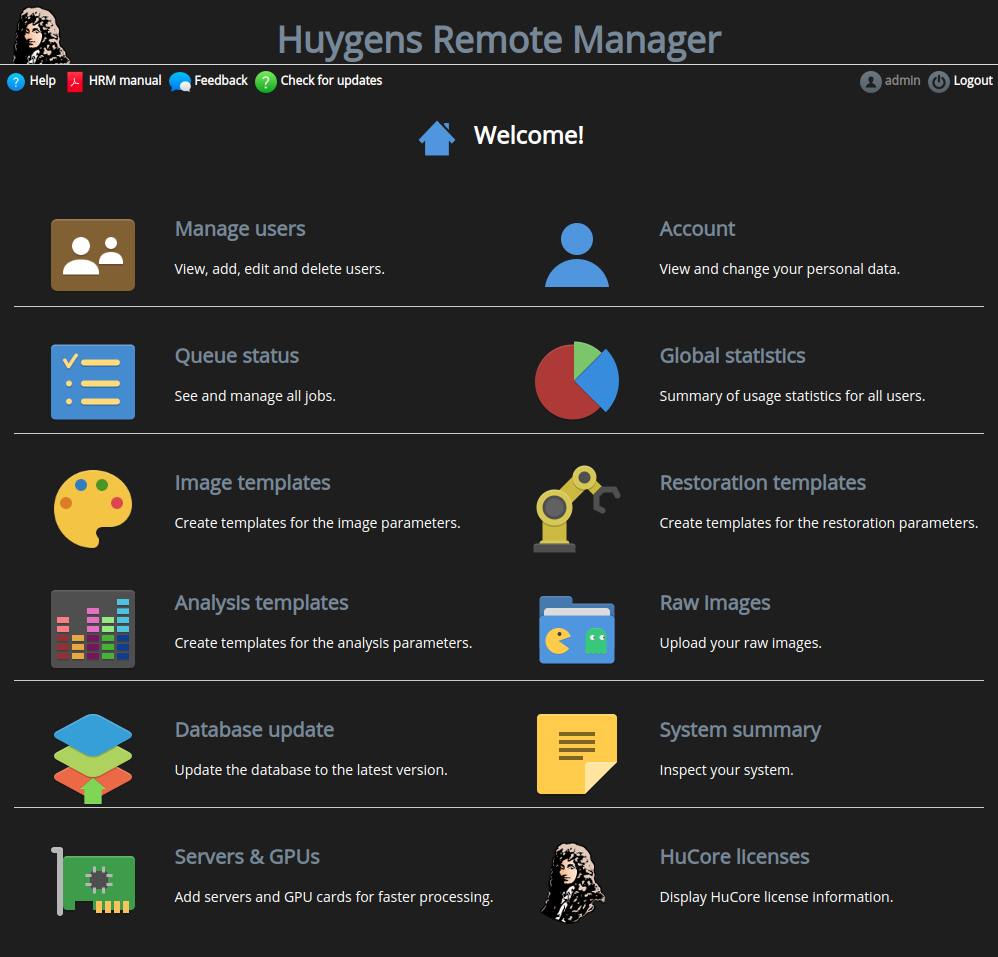
There are a number of extra options that are available to the administrator only:
- Manage users: Add, remove, edit, enable and disable users. Alternatively, HRM allows for LDAP/Active Directory user management.
- Queue status: Manage jobs from all users.
- Global statistics: See statistics from all users and jobs, including microscope types, PSFs, research groups, dates, etc.
- Database update: Carry out a database update when a new HRM release requires it.
- System summary: Get an overview of all the versions and configuration options that play a role in HRM.
- Check for updates: Get automatic feedback on whether you are running the latest HRM version.
- Create global templates: The administrator can create global templates accessible to all users. This is meaningful for lowering the threshold for those beginning users who need assistance to start deconvolving their raw data. Global templates can be created at any of the states where templates are required: The Image Parameters (2/5), The Restoration Parameters (3/5) and Analysis parameters (4/5).
- Servers & GPUs: Add and remove processing machines and GPU cards. This has an effect on the total number of jobs that can run in parallel.
- HuCore licenses: Get an overview of the installed Huygens license.
Version upgrade¶
Note
Before upgrading HRM please proceed to backup the HRM database, images and source files.
To upgrade to a new version, download the latest version from here. Then follow the intructions on specific version upgrades.
Database update¶
Note
The HRM database should NOT be deleted and replaced by a newer version.
The HRM database contains the existing users, statistics, parameter
templates, etc. To update these contents to the latest release click on
Database Update  from the admin
home panel and follow the instructions.
from the admin
home panel and follow the instructions.
In order for this update to work properly it is advised to upgrade the HRM source code before upgrading the database.
System configuration¶
HRM can be configured during the installation. The configuration settings are saved in a configuration file. Some settings, as the maximum upload limit, need to be adjusted both in HRM and in PHP.
For example, if the PHP configuration file states a max upload file size of 256MB, this is applicable to all programs using PHP. Suppose the HRM settings state that the max upload limit is 200MB, since 200MB is lower than 256MB, the HRM configuration does not conflict with the PHP configuration and 200MB is the maximum allowed file size.
Note
The PHP configuration file: /path/to/php/php.ini
The HRM configuration file: /path/to/hrm/config/hrm_config.inc
How HRM communicates with Huygens Core¶
For each deconvolution task in the job queue the HRM queue manager automatically generates a Huygens Batch template for Huygens Core that
- loads the raw image from a source directory,
- applies the microscopic parameters to it as defined by the user or reads the microscopic parameters from the image metadata,
- optionally loads another image containing the microscope Point Spread Function,
- deconvolves the image using the restoration parameters chosen by the user,
- optionally applies a chromatic aberration correction,
- optionally stabilizes the time series,
- optionally computes the colocalization coefficients of multi-channel images and generates colocalization maps,
- stores the resulting restored image in a destination directory,
- generates several visualizations of the raw and deconvolved images for the user to see the effect of the restoration,
- and finally writes a tag in the destination directory to inform the HRM queue manager that the job is finished.
When the job is finished the queue manager optionally sends the user an e-mail announcing the end of the job and its status. The administrator may configure this.
Multiple jobs can be processed in parallel depending on how HRM is configured, the multiprocessing capabilities of the server, the number of available computation servers and GPU cards.
Tips & Tricks¶
- Use the global statistics to get an idea on which microscopes are used most, which file formats, PSFs, etc.
- On the home panel, click on System summary
 to get an
overview of your current HRM settings. Expand this information with the
PHP settings and/or test the HRM e-mails by clicking on
to get an
overview of your current HRM settings. Expand this information with the
PHP settings and/or test the HRM e-mails by clicking on  .
. - When performing an HRM upgrade disable all users first. Upon successfully upgrading HRM enable the users back again.
- If you experience unexpected behaviour from the HRM queue manager, such as a deleted job which persists in the queue, restart the HRM daemon.
- Encourage your users to save deconvolved data in ICS or HDF5 formats since the dynamic range and metadata parameters are conserved (unlike in TIFF). Moreover both ICS and HDF5 allow for good compression rates.
Clean a Stalled Queue in HRM¶
It could happen that the queue breaks or freezes and the database is polluted with outdated information.
To fix this, one must currently go and clean up a few places in the hrm database as well as restart the queue manager. Here is a short checklist of what to do.
- shut down the hrm daemon by using
sudo /etc/init.d/hrmd stop
or
sudo systemctl stop hrmd
go to the
hrmdatabase and do the following- Remove broken or killed jobs from the
job_*tables - Make sure that the
servertable has a status of ‘free’ and job set to NULL
Both measures can be achieved with the following SQL script:
- Remove broken or killed jobs from the
DELETE FROM job_analysis_parameter WHERE setting IN (SELECT id FROM job_queue WHERE status="broken" OR status="kill");
DELETE FROM job_analysis_setting WHERE name IN (SELECT id FROM job_queue WHERE status="broken" OR status="kill");
DELETE FROM job_files WHERE job IN (SELECT id FROM job_queue WHERE status="broken" OR status="kill");
DELETE FROM job_parameter WHERE setting IN (SELECT id FROM job_queue WHERE status="broken" OR status="kill");
DELETE FROM job_parameter_setting WHERE name IN (SELECT id FROM job_queue WHERE status="broken" OR status="kill");
DELETE FROM job_task_parameter WHERE setting IN (SELECT id FROM job_queue WHERE status="broken" OR status="kill");
DELETE FROM job_task_setting WHERE name IN (SELECT id FROM job_queue WHERE status="broken" OR status="kill");
DELETE FROM job_queue WHERE status="broken" OR status="kill";
UPDATE server SET status= 'free', job = NULL;
- restart the hrm daemon
sudo /etc/init.d/hrmd start